

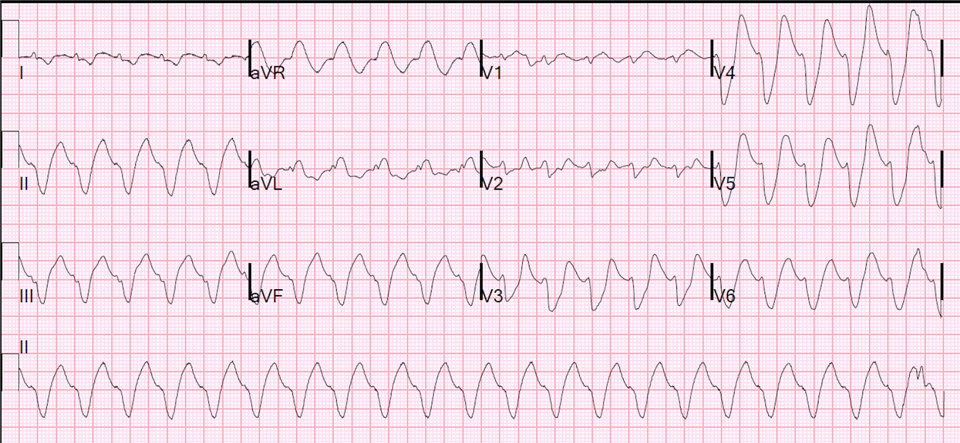
May be present with hypertonicity caused by other agents such as mannitol (Osmitrol) as well.Ĭan cause hyperkalemia in patients with decreased renal function inhibits adrenal aldosterone synthesis Hyperkalemia may occur with continuous infusions or with boluses of hypertonic glucose. Hypertonicity caused by hyperglycemia from glucose infusions can drive potassium out of the intracellular space, leading to hyperkalemia. Suppresses renin release, leading to decreased aldosterone synthesis, decreased potassium secretion in collecting ductĭecreases sodium-potassium ATPase activityĭecreases aldosterone synthesis most common in patients on dialysis who drink water with high fluoride levels Inhibits adrenal steroid synthesis, which can lead to aldosterone deficiencyĭecreases sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) activity beta 2 agonists decrease potassium levels Lysine, arginine, or epsilon-aminocaproic acid enters cells in exchange for potassium, causing hyperkalemiaĭecreases aldosterone synthesis hyperkalemia often can be reduced by concomitant diuretic use ARBs less likely to cause hyperkalemia than ACE inhibitors Sodium polystyrene therapy, sometimes with intravenous furosemide and saline, is then initiated to lower total body potassium levels.Īmiloride (Midamor) and triamterene (Dyrenium)ĭiminishes potassium secretion by reducing the electrical gradient between the intracellular space and the renal tubule, causing potassium to leave the cells Serum potassium levels can be lowered acutely by using intravenous insulin and glucose, nebulized beta 2 agonists, or both. Intravenous calcium is effective in reversing electrocardiographic changes and reducing the risk of arrhythmias but does not lower serum potassium. Urine potassium, creatinine, and osmolarity should be obtained as a first step in determining the cause of hyperkalemia, which directs long-term treatment. The presence of typical electrocardiographic changes or a rapid rise in serum potassium indicates that hyperkalemia is potentially life threatening. In patients with diabetic nephropathy, hyperkalemia may be caused by the syndrome of hyporeninemic hypoaldosteronism. Acute episodes of hyperkalemia commonly are triggered by the introduction of a medication affecting potassium homeostasis illness or dehydration also can be triggers. Hyperkalemia is a potentially life-threatening metabolic problem caused by inability of the kidneys to excrete potassium, impairment of the mechanisms that move potassium from the circulation into the cells, or a combination of these factors.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
